Nanotechnology: A Frontier in Space Exploration
Priyanka Kasturia
“Nanotechnology is a new way of thinking about space missions. Once the idea is out there, people will think of its enormous applications.”
McInnes
Nanotechnology, the technology of nanoscales, is emerging as a frontier, and one of the rapidly increasing current research domains is gaining its attention towards space exploration. McInnes once said, “Nanotechnology is a new way of thinking about space missions. Once the idea is out there, people will think of its enormous applications.” The way nanotechnology is coming out with its mind-blowing applications, those words were exact.
While thinking about future space science, the ideas of space elevators and future colonization were seemed to be impractical. But, nanotechnology, when came into the picture, has given these concepts a vision of possible reality in the future. The goal of making space missions cost-effective, more reliable, and comfortable, and becoming an interplanetary species could be possible with the applications of nanotechnology
NanoFET: Replacing the Chemical Propulsion System
The present technology is based on the chemical propulsion system, by which we have successfully sent several satellites and space probes out of the Earth’s atmosphere. For such propulsion, the reactions between chemicals from the burning or oxidizing a fuel provide the thrust along with heat. But, they are much costly, $152 million per month as an average cost of NASA’s rocket launch. Moreover, about 95% of the fuel gets wasted, and only 5% is left for space travel.
Electric Propulsion (EP) is another propulsion system, which has an aim to reduce the propellant mass, increasing the payload capacity, and decreasing launch mass, and works on the principle of the use of electric power to accelerate the propellant.
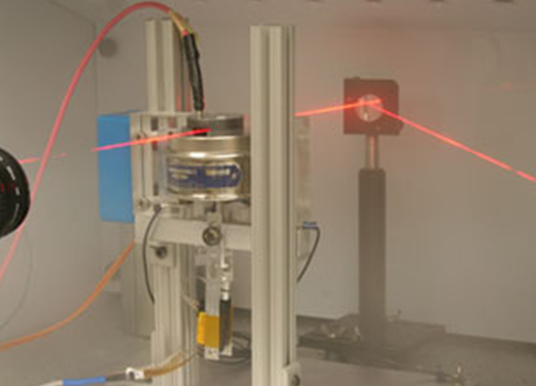
NanoFET is one such improved and new electric propulsion that requires accelerated nano-particles along with electrically charged ones, in which, the thruster arrays of high scales would be fabricated by fitting the millions of micro-sized nanoparticle thrusters on one square centimeter. The emission of these particles would provide the thrust to the rockets. In this, the particles would be stored in the cylindrical Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) that can be present in the tanks. The output of the thrust can be varied by changing the size of the particles, as nanoFET would vary its fuel efficiency.
But, the benefits and applications of nanoFET also come with several challenges, one of them, is to deal with the problem in transporting the particles to the charging pad. For now, it is under development at the University of Michigan’s Plasmodynamics & Electric Propulsion Laboratory, but, in the future, it could contribute to the goal of cost-efficient space missions
Space Elevator: Planet-to-Space Transportation System
Can you think of a cable kind of system, which could take you to space, full of darkness and fascination? Probably you couldn’t, but, in 1985, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky thought of this and published the concept in his first publication. Though it sounds like a sci-fi idea, today’s nanotechnology has given us a way to make it a reality by preferring carbon nanotubes as a promising material with its amazing properties, being lightweight and durable. Well, there are other candidates also like, Boron Nitride Nanotubes and Diamond Nanothreads, as they match the requirements of the efficient cable.

So, the main component of the elevator is the cable (or tether) that would extend from the earth to the geosynchronous satellite orbit in space, above 22,000 miles. The elevator would consist of a monitored system of pods (elevator pods), which would move up and down, capable of taking space probes, satellites, and humans, even without the use of rockets.
“Construction is not feasible today, but it could be towards the end of the century, and for that, first, we have to develop the technology.”
Smitherman
In 2018, the STARS-Me space elevator experiment was done by researchers at Japan’s Shizuoka University by connecting two CubeSats with tether into space, which was successful. So, there is a possibility to look for future elevator developments, and according to Smitherman, “Construction is not feasible today, but it could be towards the end of the century, and for that, first, we have to develop the technology.”
Solar Sail: Go with the controlled-flow of photons
I’m sure you know the sailor ship, the one who moves with the direction of the wind, and there is a person who controls its movement. The idea of a solar sail is something like that. Instead of oceans, the darkness of space would be there. The wind would be replaced by the pressure of solar radiation.
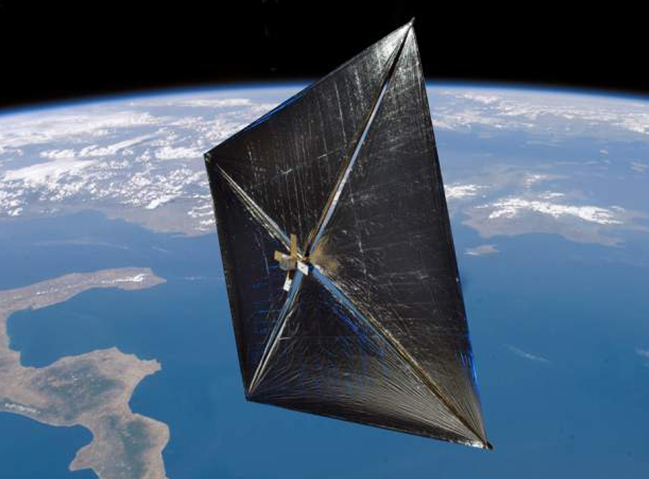

The solar sail has a large surface area, extremely reflective, thin & lightweight body that works on the momentum of the emitted photons from the sun. Here, the thrust is created by the pressure of solar radiation on the highly reflecting surface. Thus, the momentum of the photon emerges as energy to make the sail to move forward. Japanese Space Exploration Agency’s Interplanetary Kite-craft Accelerated by Radiation Of the Sun (IKAROS) spacecraft and NASA’s NanoSail-D has already used this technology for their space exploration programs. So, why do we need nanotechnology there?
For the solar sails, the material must have a large surface area, extremely reflective surface, and should be lightweight, and all these requirements can be fulfilled by the nanotechnology. The use of Carbon Nanotubes can be a possible solution because of its properties such as high tensile strength, high flexibility, large surface to volume ratio, etc.
For high reflectivity, the advanced nanomaterial could be designed in the future. Also, the goal is to develop self-healing properties of the material, which can be done by nanotechnology. So, the Carbon Nanotubes are currently used by researchers at the University of Texas to replace the current polymer sheets.
Nanobots: To enhance our planetary exploration experience
Nanorobots or nanobots are the nano-sized, intelligent robots that are efficient enough for actuation, sensing, signaling, information processing, and swarm behavior, and would help to make the future exploration more efficient. Though they are small in size, still, their capabilities are big enough to provide us a more reliable and a better experience.

So, let’s begin with the primary need for human space flight, Radiation Shield. Though we are surrounded by the radiations, still, the ones that we experience in our daily life are different from space radiations. As humans will leave the protective blanket is the Earth’s atmosphere, he would interact with the ionization radiations, causing harm to the body, and eventually, the long term exposure would increase the risk of cancer and DNA damage.
So, the isotropically enriched Boron Nitride Nanotubes emerged as a possible solution in front of scientists. It has a high radiation shielding property that would work as an extra shielding to the space craft & human cargos, which would be cost-effective, robust, and lightweight.
Since we are talking about protection, then, it would be really nice if we have spacesuits that would protect us in the harsh space environment, and could be able to repair itself. So, the Marssuit Repair Nanorobots (MRN) is the robots that could be actively used in spacesuits to self-repair themselves in case of any damage to the Marssuit.
Also, bio-nano robots’ layers can be included to provide biological protection to astronauts. The All-Terrain Bionano (ATB) Gears are the three-layered gears for Astronauts, in which, the inner layer is for body protection, the middle layer would be responsible for communicating, signaling & drug delivery, while, the outer layer is for sensing the external environmental conditions.
The smart cloth would be one of the astonishing products of nanotechnology that wouldn’t act only like a flexible cloth-like material of swarms, but also would have a nanocomputer for specific functions like, keeping astronauts from bouncing around inside their spacecraft during their sleep.
The exploration of super hot planets like Venus can be done with the nanobots. The surface temperature of Venus is so high that it becomes difficult with the present technology to get the data for research, as the temperature is about 464-degree Celsius over there, which can even melt the Lead. So, we need such materials that can withstand this high temperature, and nanobots made up of silicon nanomaterials are capable of doing so.
Other than Venus, nanobots are also capable of collecting and sending the data for the turbulent gaseous planets such as Jupiter and Saturn. The chemical composition, planet morphology, and the atmosphere can be studied in a much better way.
Nanotechnology: Emerging as a way for Space Colonization
“The big size of the robots is a problem when it comes to space exploration for future colonization. So, robots should be made extremely small instead, which can be possible with nanotechnology. ” – this sentence is sufficient to describe the role of nanotechnology for space colonization.
The exploration of the surface is essential to set up a space colony. So, nanosensors are highly appropriate for a few specific tasks such as looking for water, other chemicals, different minerals, traces of oxygen & biological life, and even can burrow into the surface for inspection at the molecular level.
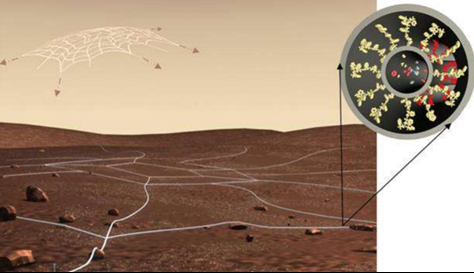
The spider web – sensor net is one such idea proposed by a team from Northeastern University, working to look for possible techniques and nanoscience in space exploration. In this, the hair-like tubular structures, comprised of nanorobots, are arranged in a web-like-net that would deploy to the entire surface to look for surface temperature, chemical composition, and other elements of the planetary environment. Networked TerraXplorers (NTXp), is another nano-device & kind of net, which would be useful for mapping and sensing vast planetary terrains, so that, they will identify the presence of chemicals and water by interaction with the planetary surface, and give us relevant information.
Coming back to the nanorobots, the swarms could be highly beneficial for our purposes as they can be scattered so that they can explore the planet’s surface, and through the atmosphere to perform experiments and do surveys quickly. Though Mars Rovers – Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity were successful, a few shortcomings like the slow speed movements, and taking a long time for communication were also there. So, the large and heavy rovers could be replaced with nanorobots for efficient work.
Along with the Artificial Intelligence (AI), the functioning of the robots would be limitless, and they can perform several things such as testing for toxicity or measuring radiation, setting up a communication system to send data back to the Earth, and collect data for minerals and elements present there.
Not only to the surface study, but nanobots would also be beneficial for construction purposes. A few properties of them, being self-replicable, utilization of the elements and resources to convert them into usable energy, and monitoring the activity over there could be highly useful to start with the construction of buildings and laboratories. Also, a team of scientists and engineers can check up on the progress via telepresence, utilizing cameras and sensors.
[…] Suggested Reading: Nanotechnology: A Frontier in Space Exploration […]